Retail surveillance is becoming smart.
The hybridization of traditional retail surveillance with AI-based video analytics is fast becoming the norm. Retailers are driving success through measurable and actionable insights delivered by retail analytics.
But if you’re new to all this—where do you start?
A great starting point is understanding how and why retail surveillance is driving innovation through intelligent video analytics (IVA) and the top 10 strategies you can adopt for success.
The Future of Retail Surveillance – Intelligent Video Analytics
Smart retail utilizes IVA to record, analyze, and aggregate real-time customer data and leverages dashboards to deliver actionable insights to craft the best customer experience, which boosts sales.
IVA enables decision-makers to make critical business decisions to improve:
- Operational efficiency
- Product placement strategies
- Store layout optimization
- Theft detection and prevention
But how exactly is this achieved? Here are ten strategies in smart retail surveillance that give businesses the insights they need to succeed.
The Top 10 Strategies in Smart Retail Surveillance
1. People Counting
People counting tracks the number of customers that enter the store or are within a defined region of the store.
With this data, managers can analyze how dimensions like advertising, displays, time of day, day of the week, location, etc. influence the frequency of visits.
2. Entrants Vs. Passerby Surveillance
IVA can identify and distinguish the number of shoppers entering your retail outlets compared to foot traffic walking past.
This gives insights into the amount of foot traffic passing your stores versus how much is entering.
3. Dwell Time Surveillance
Retailers use dwell time to determine how long a customer stays within a pre-defined store, department, or region.
This data offers insights into what displays and products pique a customer’s interest and how much time they spend deciding on a purchase.
4. Occupancy Time Surveillance
With the occupancy time IVA, retailers can determine how long customers stay in different areas of their stores. In addition, occupancy time data is fed into heatmaps, which visually display store areas with the most foot traffic, with red and orange regions representing higher rates of foot traffic activity.
Businesses use occupancy time and heatmaps to analyze peak and non-peak times to optimize operational efficiency further, which we will discuss later.
5. Intrusion Detection & Prevention
IVA allows retailers to detect unauthorized customers and staff in predefined areas. This aids in detecting unauthorized access to restricted areas, suspicious loiterers, and blocklisted people.
This can help prevent break-ins and customers or staff from entering sensitive or dangerous parts of your business premises.
6. Merchandise & Aisle Activity
Understanding which areas of a store are visited more than others is paramount for the success of any retailer.
While sales tracking software can offer insights into what customers purchase, it is vital to understand where customers make their purchasing decisions in-store.
Merchandise and aisle activity offers these insights and allows retailers to analyze what areas of their stores are busier than others and how to prevent bottlenecks of customers with better product placements to improve customer flow and the overall shopping experience.
7. Age and Gender Demographics
Retailers that don’t understand their customers can’t sell to them, and a key data point for success is demographic market analysis. Smart retailers utilize IVA to track variables such as age and gender to gain insights.
Dimensionalizing age groups and genders lets smart retailers tune shopping experiences to match demographic product preferences.
8. Heat Mapping
Fuelled by people counting, dwell time, occupancy time, merchandise, and aisle activity, customer heat maps give retailers a visual representation of “hot” and “cold” zones for customer activities.
Analytical heat maps track customer traffic concentration and the resting zone by tracking customer paths and occupancy time.
This data is essential for managers to manage staff and tune customer experiences and advertising efforts.
9. Multi-store Operations Management
Managing multiple stores requires a centralized database to streamline business operations and analytics.
Smart retailers utilize multi-store operations management tools with online dashboards to record, analyze, and report on store traffic management, performance, and popular product zones across stores.
These tools can give retailers real-time data on how stores’ opening and closing hours, weather, time of day, day of the week, time of year, purchase patterns, and demographics affect business success and which stores are their top performers.
10. Smart Retail Business Intelligence Dashboards
While the data collection and analysis process is complex, the ability to consume insights shouldn’t be. Analytical dashboards are critical for displaying actionable insights with supporting data points.
Innovative retailers now use business intelligence dashboards that feed customizable retail data points into one consolidated display.
These insights empower decision-makers to boost store operational efficiency by optimizing customer experiences in near real-time.
Such dashboards help managers to understand how cross-store campaigns perform and make real-time adjustments across the organization for enhanced business outcomes.
How Does Smart Retail IVA Work?
Smart retail IVA works in four steps to monitor customers, collect and analyze data, store, and report main findings. These steps go as follows:
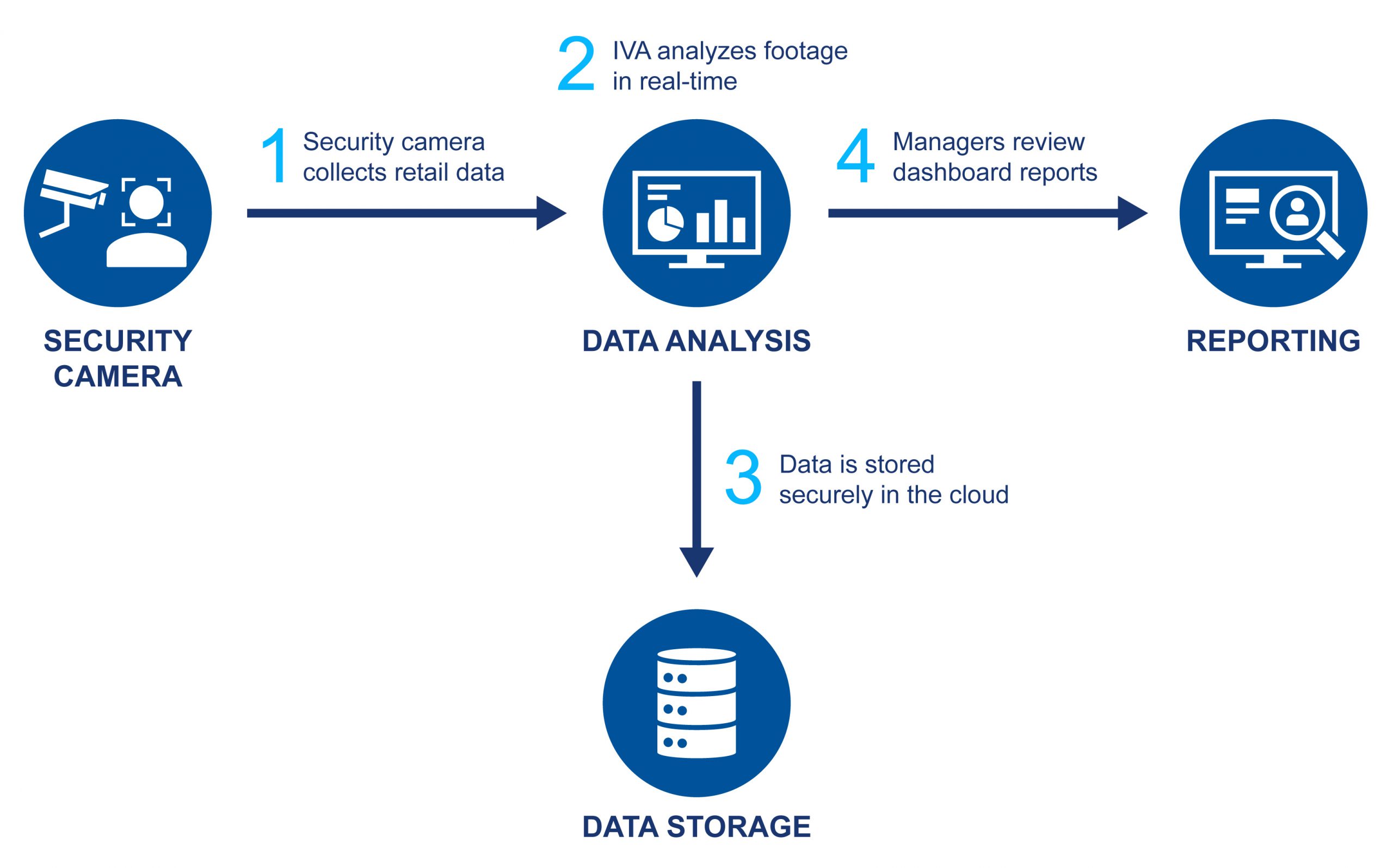
Step 1: Retail Data Collection
Surveillance and security cameras monitor areas, and the video is fed into IVA software.
Step 2: Retail Data Analysis
IVA performs comprehensive analytics on the footage in real-time to produce data points such as the number of customers, merchandise activity, aisle traffic, dwell time, and age & gender analysis.
Step 3: Data Management & Storage
Retail data points are then stored securely in a cloud, in an on-premise server, or in a hybrid cloud.
Step 4: Access & Reporting
Retail data points are presented through actionable graphs, charts, and widgets for detailed reporting on a centralized platform for managers to access and assess the necessary changes they need to drive into their business.
The Retailer’s Pathway to Business Intelligence for Success – Gorilla Smart Retail
With many strategies, retailers must adopt IVA to streamline operations and increase margins and profitability.
Gorilla Smart Retail is a comprehensive, real-time solution for your surveillance system to provide insights into top-performing store layouts, shoppers, and conversion rates by delivering actionable insights for greater business outcomes.